Introduction:
Intermittent compression massage after varicose vein therapy?
An intermittent compression massage after varicose vein therapy is not yet standard. In some cases, it is applied again and again after radical surgical or thermal op techniques. According to our experience from 32 years of our own radical surgery in the context of vascular surgery and after 19 years of work with thermal ablation (laser, radio wave), this immediate postoperative intermittent compression massage is not tolerated by the patient due to pain. We have other experiences after non-permanent, non-tumescent procedures, such as the vein glue or the sealing foam method. Here is a very good tolerance of the postoperative compression massage experience. First of all, we want to present the first impressions and experiences with this new post-surgical adjuvant therapy of CVI. For the purpose of a subjective and objective scientific analysis, we have started a prospective randomized study on this topic. This currently includes 50 patients.
Pathophysiological considerations
An inflammatory reaction is the complex response of the vascular and connective tissue to cell damage or destruction with the aim of eliminating the cause of the irritation and repairing the defects that have arisen. The general treatment goals of the compression massage are the reduction of tissue tension through reduction of oedemas, the accelerated removal of cellular debris and inflammatory mediators, the reduction of postoperative pain, as well as the attenuation of an excessive inflammatory response. In the early phase after surgical interventions, the use of manual lymphatic drainage (ML) or even better the 12 – chamber massage therapy has proven itself. These massage techniques promote the regeneration of lymph collectors in the injured area. Tissue scarring then feels softer, more resilient, and less likely to cause secondary mobility limitations. The postoperative extrinsic and muscular-like appearance are much less called by the patient.
Results
Compression massage immediately after VenaSeal – vein glue or Sealing Foam is by now in Saphenion Rostock standard in the after treatment therapy . 10 months ago, we started to perform a intermittend compression massage of the treated legs in all patients immediately after a varicose vein therapy using a vein glue or after a micro-foam therapy with Sealing Foam (sealing microfoam).
All patients gladly accepted this massage therapy of the operated legs by means of a 12 – chamber massage computer.
In the meantime, this additional adjuvant therapy is regularly in demand. Our experience with compression therapy after sealing varicose veins is consistently positive. We introduced the new supporting therapy concept 10 months ago in Rostock. So far, 120 patients have been postoperatively treated by sealing truncal varicose veins and 248 patients after a micro-foam therapy period by means of intermittent compression therapy. We were very surprised by the success of the therapy. All 120 VenaSeal patients showed significantly less hardening along the treated vein, the strand sensation was not really noticed or was noticeably less prominent after the treatment. The pain was not reported at all. The real goal, the reduction of postoperative edema, was very impressive. None of the patients reported any swelling or heaviness – on the contrary, significantly lighter legs with significantly reduced swelling of the lower leg were already reported on the first postoperative day. The micro-foam therapy patients also found the massage after the treatment very pleasant. Significantly lower post-therapeutic hardening after treatment of varicose side branches could be found here. We have not yet seen a new development of spider veins after intermittent compression therapy. For the use of the compression the compression massage therapy after tumescent anesthesia laser and radio wave, we have no current experience – we have in these cases refrained from a compression massage therapy. Radical surgical therapy procedures are no longer offered in the Rostock practice.
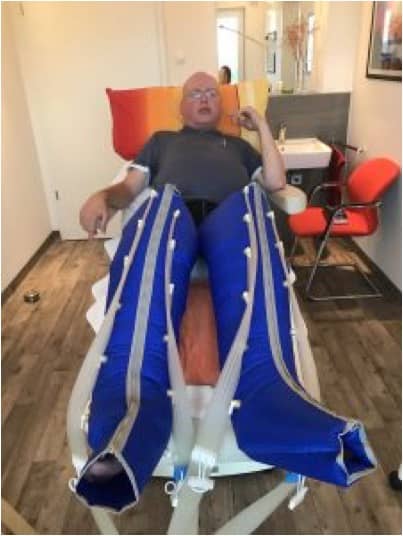
Anesthesia was not possible. Thus, the health insurance has agreed to a VenaSeal – surgery simultaneously on both legs – The photo shows the patient after the intervention in the intermittent compression therapy….
Discussion
Let us briefly quote from the guidelines on compression massage therapy in Germany:
The intermittent pneumatic compression therapy consists in the prophylactic and therapeutic use of pneumatic alternating thrusts for thromboembolic prophylaxis, decongestive therapy for edema diseases, improvement of arterial and venous blood flow with reduction of clinical symptoms and to promote wound healing … According to these guidelines, intermittent compression therapy is not included immediately after surgical rehabilitation of varicose truncal veins and varicose side branches. After extensive soft tissue defects, e.g. after radical varicose vein treatment (stripping) or even after extensive thermal irritation of the subcutaneous tissue as a result of laser or radio wave ablation, this therapy is rather contraindicated in terms of wound healing and also to avoid postoperative pain conditions! The situation is different with non-tumescent, non-thermal, non-radical forms of therapy. These cases show excellent post-operative healing effects. Also, the objective healing criteria, such as lack of instinct, significantly reduced endovenous thrombus formation and postoperative hematomas and edema are extremely positively influenced.
We will report on the results of our prospective single-center study and the subjective and objective results derived from it.
References:
1. Földi E: Das postoperative Lymphödem: Das klinische Problem: Diagnostik und aktuelle Behandlungskonzepte; Phlebologie 3 / 2011
2. Kappa Markovi R: Prospektive randomisierte Studie zur Evaluation der intermittierend pneumatischen Kompression nach Varizenoperationen; Vortrag auf der 59.Jahrestagung der DGP, Stuttgart 2017.
3. Reich – Schupke S et Schwahn – Schreiber C: Auszug aus der S1 – Leitlinie Intermittierende pneumatische Kompression; Phlebologie 5 / 2018; S. 272 – 275
4. Földi.E.: Das postoperative Lymphödem: Das klinische Problem: Diagnostik und aktuelle Behandlungskonzepte; Phlebologie 3 / 2011
5. Kappa Markovi, R.: Prospektive randomisierte Studie zur Evaluation der intermittierend pneumatischen Kompression nach Varizenoperationen; Vortrag auf der 59.Jahrestagung der DGP, Stuttgart 2017.
6. Zierau UT: https://www.saphenion.de/news/kompressionsmassage-nach-krampfadertherapie-massage-after-varicose-vein-therapy/
