Zierau, UT (1); Sell, M (2) and Lahl, W (1)
SaphenionScience: VenaSeal varicose veins – histopathological changes of tissue and veins
KEYWORDS: VenaSeal, Cyanoacrylate vein glue; Foreign body reaction; Sealing truncal varicose veins,
Abstract:
SaphenionScience: VenaSeal varicose veins: Since 7 years we are working with VenaSeal (Medtronic, Minneapolis), a N-butyl -2 – cyanoacrylate in therapy of truncal varicose veins. Until to today time we treated 2384 truncal veins. The cyanoacrylat – polymer is a high effective vein glue for the treatment of patients with CVI and varicosie veins. As an implanted device, question is important: How long cyanoacrylate persists after using as a vein glue inside the truncal varicose veins.

Introduction:
SaphenionScience: VenaSeal varicose veins: Sealing veins ist a new therapy option since 2011 in Europe and since 2015 in USA. The technique of sealing wound, tissues, bones and vessels is not new yet, already since the earlier sixties we know sealing technique in dermatology.
Since 1949 the chemical compound of cyanoacryle glue is known, first being used in operative medicine in the early 60s. All we know the tissue adhesive or replacement of wound sutures. Also the authors have used this glue during their time in trauma surgery in the 60th. to 80th.
Today it´s real – nearly all operative disciplines are using cyanoacrylate, i. e dermatology, ophthalmology, orthopedics, surgery, orthodontics, interventional radiology, vascular surgery, neurosurgery
The risk of allergic reaction is not real – we didn`t found any real report or competent scientific study in medline or pubmed. And we ourself also didn`t seen any allergic reaction in using glue over all 7 years. And also the FDA – approval states: VenaSeal® is bio – compatible / resorptive, not carcinogenic and not allergenic!
The examination in three cases
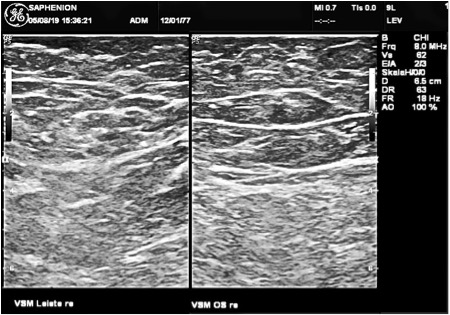
SaphenionScience: VenaSeal varicose veins: In 2017 / 2018 we saw three cases with a „glue pimple“ (nearly 2cm) above the treated and sealed varicose GSV. We thought, that these pimples were a direct reaction after sealing the veins. In one case the treatment with VenaSeal was 10 months ago, in 2 cases the therapy with the vein glue was 12 months ago.
After information the patient and getting the agreement, we have opened all the pimples with a scalpel, took a sharp spoon and peel ou all the whole content of the pimple including the pimple capsule. We sent all the material to a special institute for pathology.
Our question was: Ist there any glue inside, are there any chemical adhesive residues? The next question was: Can we find any vein structures, can we see any competent vein wall?The answer in all 3 cases was the same. You can read the result here:

Histopathology:
Pathological-anatomical examination and assessment:
Microscopy: Thigh Inner left: Two 2 cm and 5 cm gray tissue fragments. Complete embedding.
Methods: Paraffin, HE, Elastica van Gieson staining, iron.
Microscopy: The tissue was completely embedded and shows histologically compactly stored polymorphonuclear granulocytes, fibrin, and fine narrow fiber structures. The Elastic van Gieson staining also shows individual fragmented elastic fibers. In the iron coloration no proof of pigment. Assessment: signs of inflammation with individual elastic fibers (left thigh), no malignancy: The elastic fibers could correspond to parts of a venous vessel, no foreign bodies.
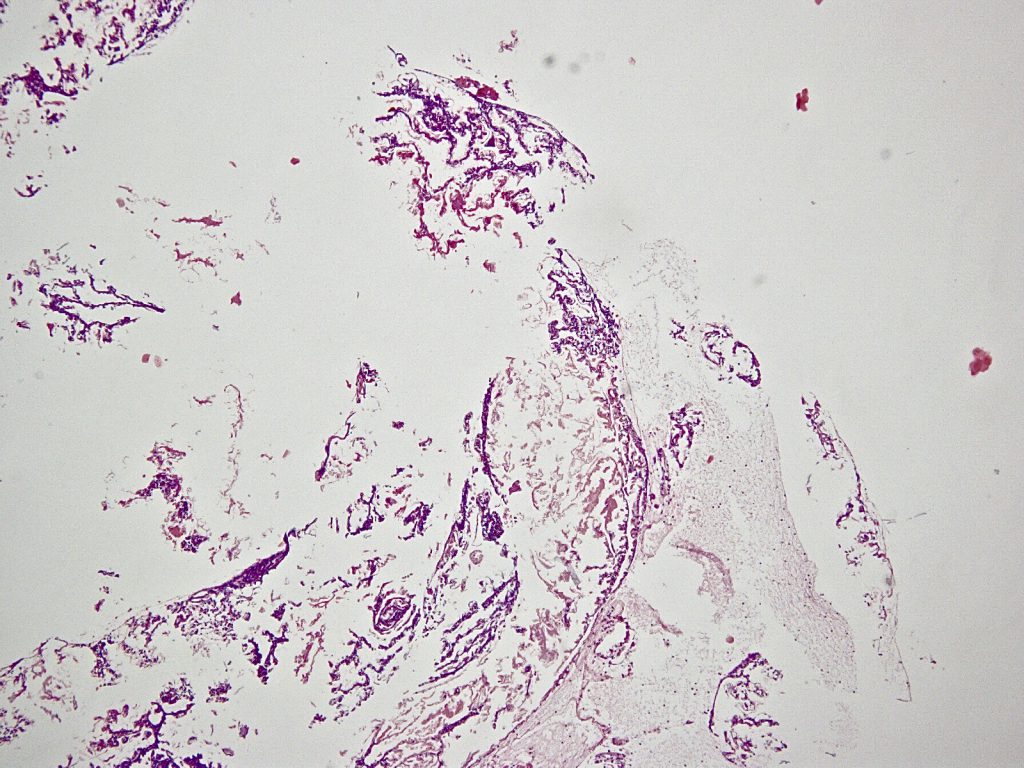
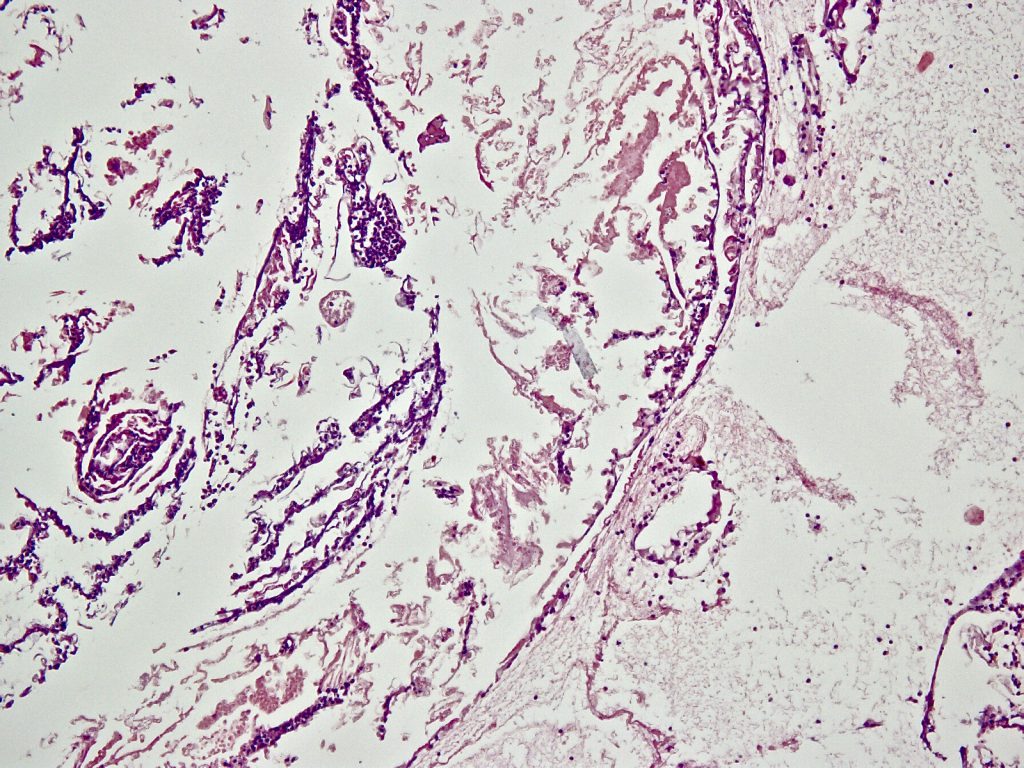
So the result was the same in all three cases: We can not find any vein wall, we can only find some elastic fibers as parts of the destroyed vein wall.
We also can not find any rest of glue or other chemical compounds from the VenaSeal mixture.
Discussions
SaphenionScience: VenaSeal varicose Veins: All we users of VenaSeal have one question: How long cyanoacrylate persists after closure? In our 3 cases the patients were examined 10 and 12 months after implantation of cyanoacrylate glue. Findings were typical of a foreign body reaction (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 16). The vessel was occluded with collagenized mature fibrous tissue and polymer remnants, which were encapsulated by multinucleated giant cells. Focal areas of granulomatous inflammation were present in the destroyed vein wall parts extending to the surrounding tissue. This is the red skin streak, we can see in 8% of all treated veins. This is not a phlebitis o superficial vein thrombosis – this is the desribed inflamation after sealing the truncasl vein.
It were to be found also parts of elastic fibers of destroyed vein wall (1, 2). We have not found any thrombosis or thrombotic reaction inside a vein structure, no recanalisation. Also foreign material from the glue was not to be found after 10 – 12 months!
So we also havn`t seen – in contrast to Novotny (2) – any recanalisation of the obturated vein section.
The results are similar all the animal tests since 1969. These tests described a chemical degradation of glue between 6 to 9 months in all animal tests. The faster reaction is justified in localisation of glue injection. Nearly all papers describe an injection in muscle tissue (8, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16) – this is tissue with better blood circulation then vein- or fat tissue.
Conclusions:
N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate that has been applied gradually degrades over the course of 10 months up to 3 years accompanied by a giant cell reaction, mild chronic inflammation and vein channel cicatrices (1,16).
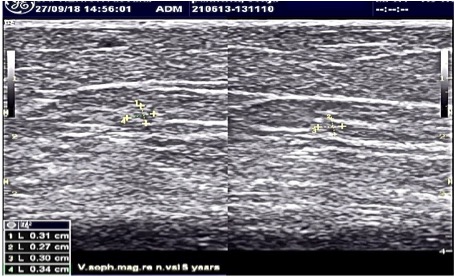
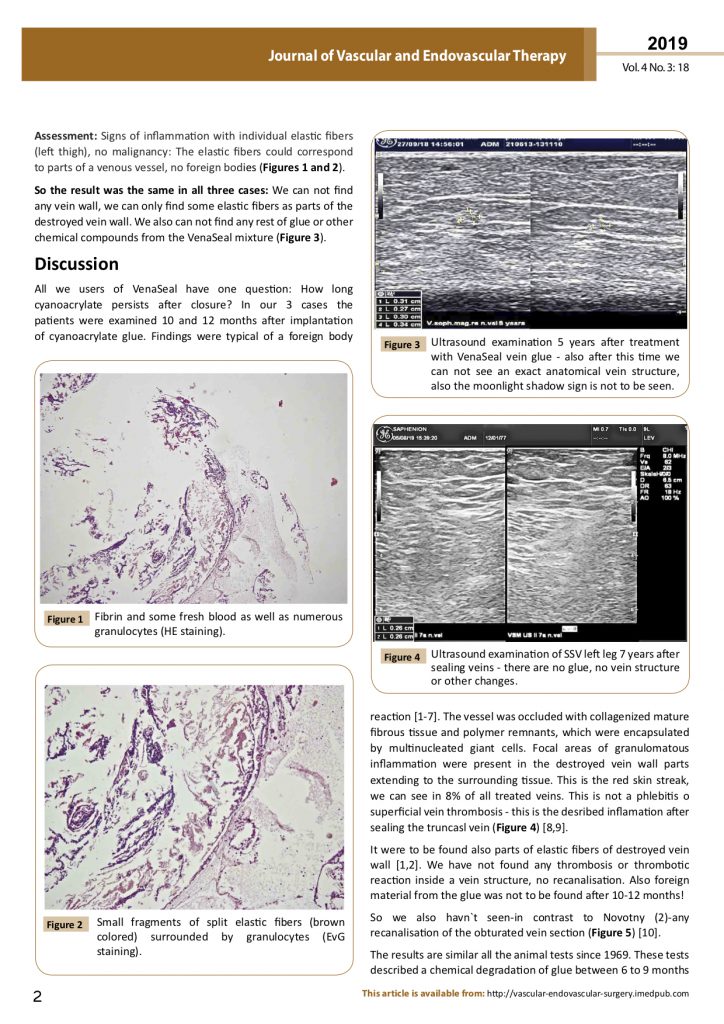
Ultrasound examination 5 years after treatment with VenaSeal vein glue – also after this time we can not see an exact anatomical vein structure, also the moonlight shadow sign is not to be seen!
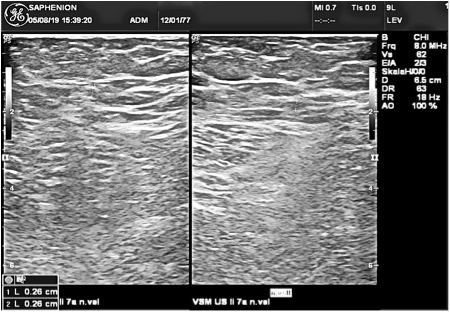
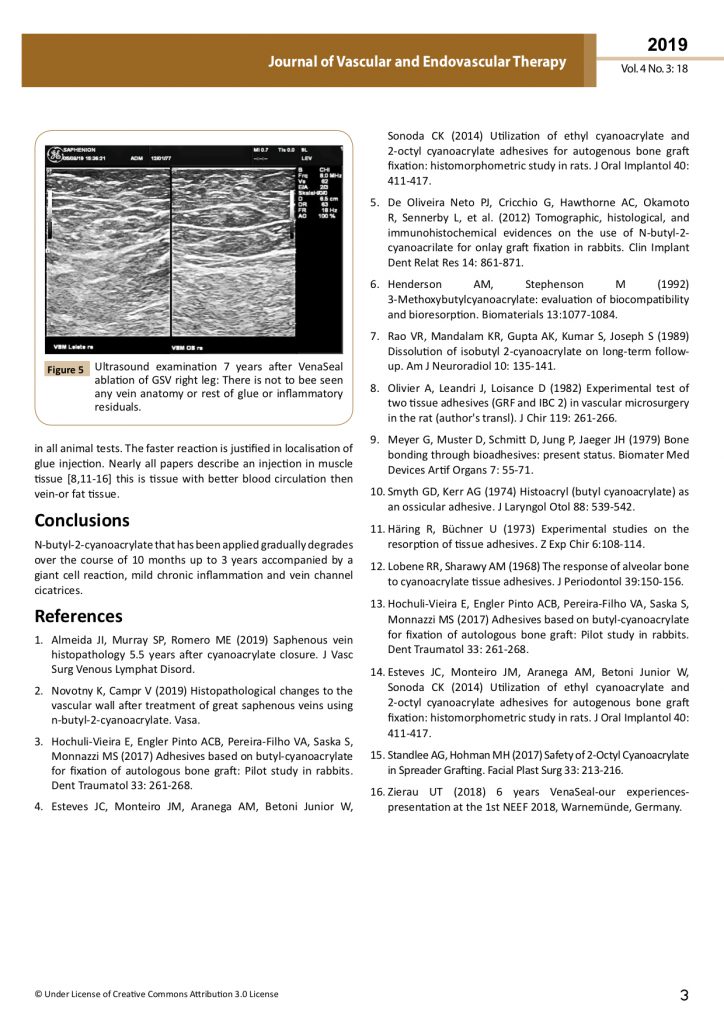
Ultrasound examination 7 years after VenaSeal ablation of GSV: There is not to bee seen any vein anatomy or rest of glue.
Links / References
1. Almeida JI1, Murray SP2
Saphenous vein histopathology 5.5 years after cyanoacrylate closure. Copyright © 2019 Society for Vascular Surgery. Published by Elsevier Inc..
Histopathological changes to the vascular wall after treatment of great saphenous veins using n-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate.Vasa. 2019 May 7:1-6. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a00079 [Epub ahead of print].
3. Hochuli-Vieira E, Engler Pinto ACB, Pereira-Filho VA, Saska S, Monnazzi MS. Adhesives based on butyl-cyanoacrylate for fixation of autologous bone graft: Pilot study in rabbits. Dent Traumatol. 2017 Aug;33(4):261-268.doi: 10.1111/edt.12328. Epub 2017 May 5. PubMed PMID: 28190302.
4. Esteves JC, Monteiro JM, Aranega AM, Betoni Junior W, Sonoda CK. Utilization of ethyl cyanoacrylate and 2-octyl cyanoacrylate adhesives for autogenous bone graft fixation: histomorphometric study in rats. J Oral Implantol. 2014 Aug;40(4):411-7. doi: 10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-12-00063. PubMed PMID: 25106004.
5. de Oliveira Neto PJ, Cricchio G, Hawthorne AC, Okamoto R, Sennerby L, Lungren S, Salata LA. Tomographic, histological, and immunohistochemical evidences on the use of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrilate for onlay graft fixation in rabbits. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012 Dec;14(6):861-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2010.00321.x. Epub 2010 Dec 22. PubMed PMID: 21176098.
6. Henderson AM, Stephenson M. 3-Methoxybutylcyanoacrylate: evaluation of biocompatibility and bioresorption. Biomaterials 1992;13(15):1077-84. PubMed PMID: 1493191.
7. Rao VR, Mandalam KR, Gupta AK, Kumar S, Joseph S. Dissolution of isobutyl 2-cyanoacrylate on long-term follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1989 Jan-Feb;10(1):135-41. PubMed PMID: 2492713.
8. Olivier A, Leandri J, Loisance D. [Experimental test of two tissue adhesives (GRF and IBC 2) in vascular microsurgery in the rat (author’s transl)]. J Chir (Paris). 1982 Apr;119(4):261-6. French. PubMed PMID: 7085811.
9. Meyer G, Muster D, Schmitt D, Jung P, Jaeger JH. Bone bonding through bioadhesives: present status. Biomater Med Devices Artif; Organs. 1979;7(1):55-71. PubMed PMID: 454783.
10. Smyth GD, Kerr AG. Histoacryl (butyl cyanoacrylate) as an ossicular adhesive. J Laryngol Otol. 1974 Jun;88(6):539-42. PubMed PMID: 4852275.
11. Häring R, Büchner U. [Experimental studies on the resorption of tissue adhesives]. Z Exp Chir. 1973;6(2):108-14. German. PubMed PMID: 4611065.
12. Lobene RR, Sharawy AM. The response of alveolar bone to cyanoacrylate tissue adhesives. J Periodontol. 1968 May;39(3):150-6. PubMed PMID: 5301229.
13. Hochuli-Vieira E, Engler Pinto ACB, Pereira-Filho VA, Saska S, Monnazzi MS. Adhesives based on butyl-cyanoacrylate for fixation of autologous bone graft: Pilot study in rabbits. Dent Traumatol. 2017 Aug;33(4):261-268. doi: 10.1111/edt.12328. Epub 2017 May 5. PubMed PMID: 28190302.
14. Esteves JC, Monteiro JM, Aranega AM, Betoni Junior W, Sonoda CK. Utilization of ethyl cyanoacrylate and 2-octyl cyanoacrylate adhesives for autogenous bone graft fixation: histomorphometric study in rats. J Oral Implantol. 2014 Aug; 40(4):411-7. doi: 10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-12-00063. PubMed PMID: 25106004.
15. Standlee AG, Hohman MH. Safety of 2-Octyl Cyanoacrylate in Spreader Grafting. Facial Plast Surg. 2017 Apr;33(2):213-216. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1597998. Epub 2017 Apr 7. PubMed PMID: 28388801.
16. Zierau, UT: 6 years VenaSeal – our experiences – presentation at the 1. NEEF 2018, Warnemünde, Germany (first presentation of histopathology in sealed veins).
Conflict of Interest: There is no conflict of Interest
Adress of authors:
1. Saphenion Venenzentrum Berlin / Rostock, Friedrichstrasse 95, 10117 Berlin. berlin@saphenion.de; rostock@saphenion.de
2. Institut für Pathologie, Berlin – Grunewald, Caspar-Theyß-Straße 27, 14193 Berlin,