SaphenionScience: Muscle veins – foot varicose veins
SaphenionScience: Muscle veins – foot varicose veins: In general, varicose vein formation of perforatorveins also causes the anatomical-functional conversion of muscle veins into varicose-vein enlarged and high-venous resting and stress-loaded muscle veins. This has already been shown by us in the impact on the capillary and arterial system:
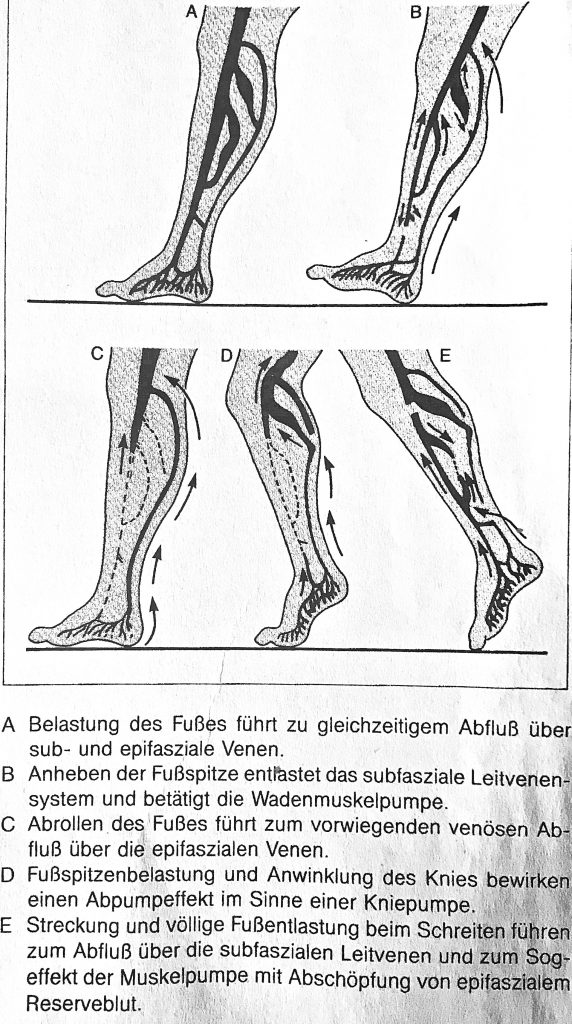
There are about 95 pairs of veins, which act as connecting veins, about 18 vein pairs are located mainly on the lower leg. These lower leg veins have a high clinical relevance – one also speaks of „surgically relevant connecting veins (May) – key perforators“.
What is important, however, is the fact that these perforator veins on the instep and ankle are already created in the normal anatomy and physiology without venous valves!
SaphenionScience: Muscle veins – foot varicose veins – The perforator veins
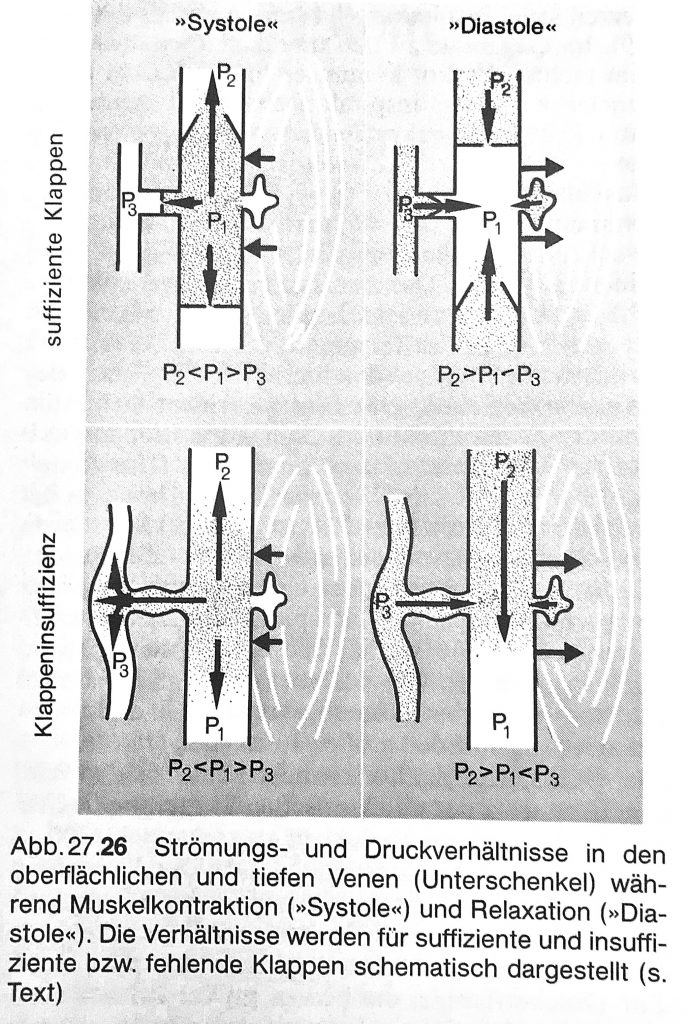
The special significance of perforator veins is that they are interconnections, through which the entire venous blood flowing above the muscle fascia is drained into the muscle veins and deep guide veins. If the venous valves of the connecting veins are also defective (perforator varicosis), local pathological changes of the muscle veins and also the expression of a regional varicosis occur. This regional varicosis and the pathologically altered muscle veins potentiate the effects of an existing general chronic venous insufficiency locally and regionally dramatically.
There are local and regional skin and tissue changes, such as fatty tissue hardening, deposits of blood breakdown products and a highly fragile skin – this is very vulnerable even at low external influences (ulcus cruris) and the healing process is dramatically prolonged.
SaphenionScience. Muscle vein-foot varicose veins – foot back varicose veins
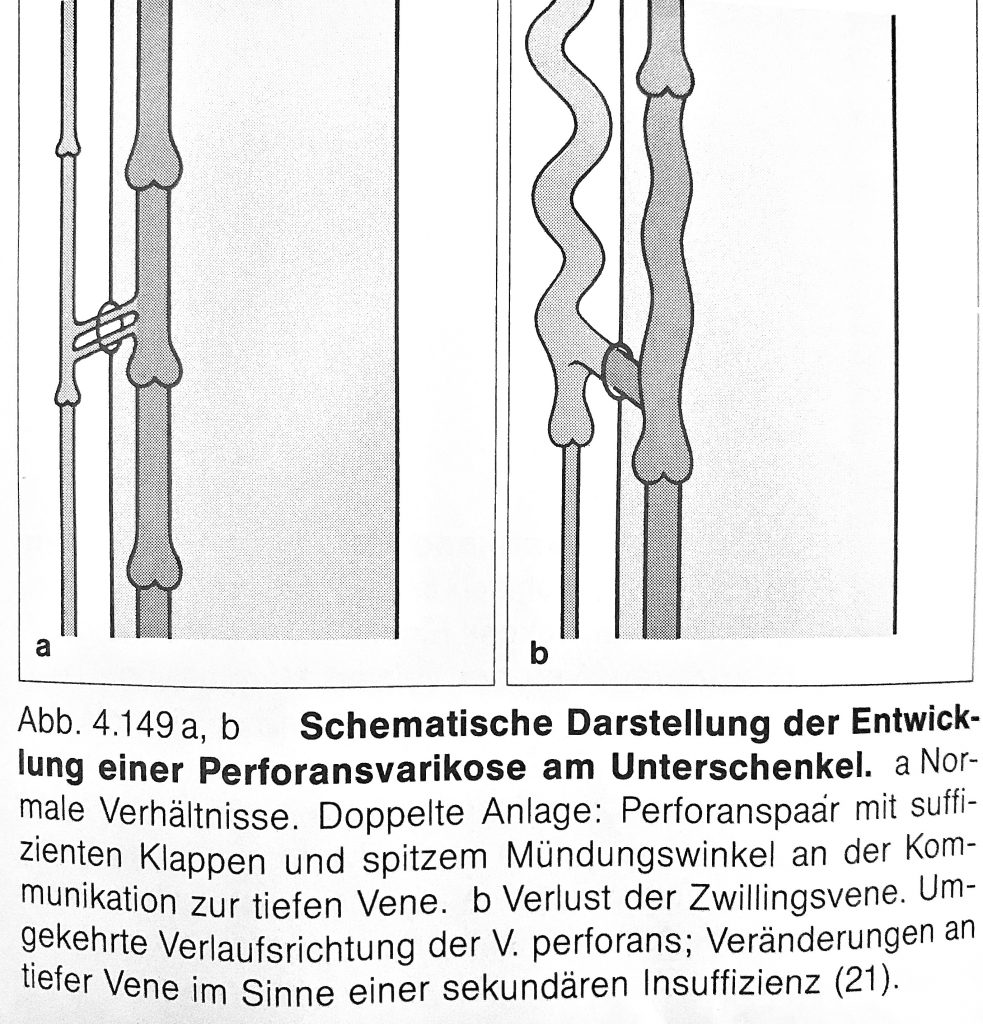
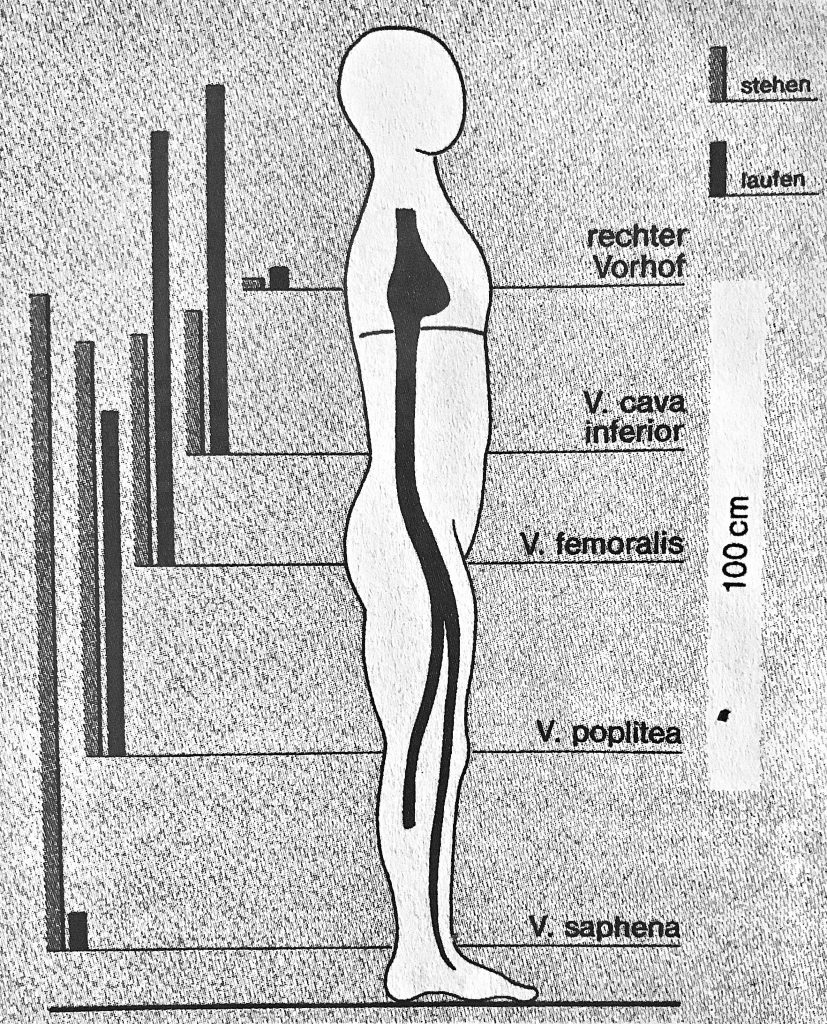
The venous pad of the sole of foot drains the venous blood through flapless (!) perforator veins to the superficial pelvic veins. The absence of venous valves is an important prerequisite for the function of the venous foot pump as well as for the special pump function in the ankle/ ankle area. However, at the exit points of the connecting veins on the dorsum and ankle, varicose veins – the so-called dorsum – and ankle varicosis develop very quickly.
However, at first disregarded in the field of venous medicine, these ankle and ankle spurs also have great clinical significance in the development of varicose on the lower leg and the development of the „open leg“ (ulcus).
The venous pad of the sole of foot drains the venous blood through flapless (!) perforator veins to the superficial pelvic veins. The absence of venous valves is an important prerequisite for the function of the venous foot pump as well as for the special pump function in the ankle/ ankle area. However, at the exit points of the connecting veins on the dorsum and ankle, varicose veins – the so-called dorsum – and ankle varicosis develop very quickly.
SaphenionScience: Muscle veins – foot varicose veins. Therapy options
After first treating the dorsal and/or ankle spurs therapeutically, today the therapist’s attention is no longer limited to the pharynx. With the introduction of ultrasound-guided vein punctures and local therapy by means of laser, microfoam or vein glue, the ankle and foot pains varicosis have come into the focus of the therapy.
However, at first disregarded in the field of venous medicine, these ankle and ankle spurs also have great clinical significance in the development of varicose on the lower leg and the development of the „open leg“ (ulcus).
The venous pad of the sole of foot drains the venous blood through flapless (!) perforator veins to the superficial pelvic veins. The absence of venous valves is an important prerequisite for the function of the venous foot pump as well as for the special pump function in the ankle/ ankle area. However, at the exit points of the connecting veins on the dorsum and ankle, varicose veins – the so-called dorsum – and ankle varicosis develop very quickly.
It is now the principle that after the treatment of truncal varicose veins also the perforator varicose veins, the ankle, and food varicose veins are to be treated. The technical possibilities of not performing this therapy radically and without a scalpel have improved considerably in the last 20 years.
Treatment of the dorsal and ankle veins by microfoam and the therapy of the perforator veins sonography supported by microfoam, laser or vein glue are standard in good medical practices.
As an interesting therapy option now comes the non-invasive SONOVEIN system. In addition to the therapy of perforator veins, the local therapy of refluxive and greatly expanded muscle veins should no longer be a problem – without cutaneous incision or puncture and the involvement of foreign bodies (microfoam, glue)
SaphenionScience: Muscle veins and foot varicose veins – Compression Stockings?
From our point of view, it is important to ensure that NO compression stockings or compression tights with an OPEN toe should be worn if there is an ankle and ankle spasm. These increase the pathological effect and lead to a massive forefoot congestion!

.
Photos/Graphiken:
Utzius: Berlin light games
Weber und May: Funktionelle Phlebologie
Literatur / Links:
Siegenthaler, W.: Klinische Pathophysiologie; Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart New York 1987.
Weber, J. und May R.: Funktionelle Phlebologie; Georg THieme Verlag Stuttgart, New York, 1990.
Danneil,O.; C.Kern und M.Stücker: Tiefe Muskelvenenthrombose nach Sklerosierung eines Seitenastes unter laufender Therapie mit Tamoxifen; vasomed 5, 2019.
